

⇒ a/b + (-a/b) = 0, here the additive inverse of a/b = (-a/b)Īnd, a/b x b/a = 1, here the multiplicative inverse a/b = b/a 3/4 x 1 = 3/4 (Multiplicative Identity)Īccording to Identity property, for a rational number a/b, its additive inverse is -a/y, and b/a is its multiplicative inverse.1/3 x (1/6 + 1/7) = (1/3 x 1/6) + (1/3 x 1/7)Īccording to Identity property, 0 is an additive identity and 1 is a multiplicative identity for rational numbers.⇒ a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c), here a and b are 2 rational numbers ⇒ a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c, here a and b are 2 rational numbersĪccording to this property, the multiplication of a whole number is distributed over the sum of the whole numbers. Rational numbers have the associative property for only addition and multiplication. ⇒ a + b = b + a, here a and b are 2 rational numbers However, this property does not hold for subtraction or division of 2 rational numbers.
Rational numbers are commutative under the operations – addition and multiplication.

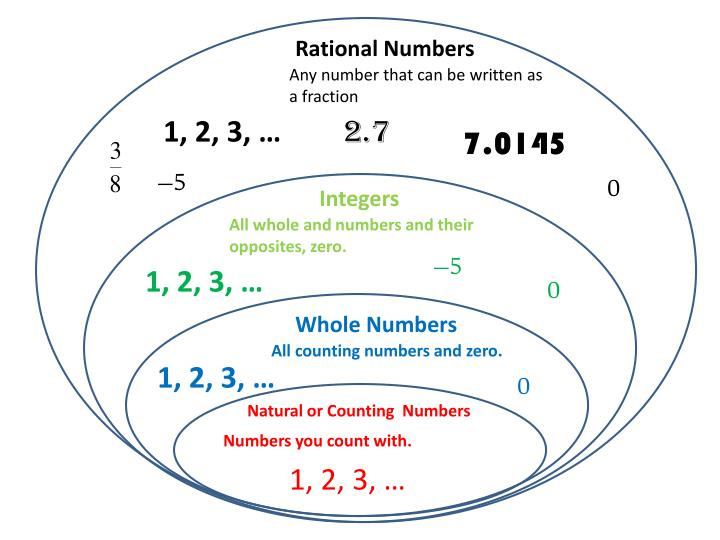
In simple words, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of 2 rational numbers ‘a’ and ‘b’ give a rational number. Rational numbers are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations. The rational numbers are universally represented by the symbol ‘Q’. Given below are some examples of rational numbers: Rational Numbers Examples of Rational Numbers


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
